JEWEL SCHOOL
- DIAMONDS 101
- PEARLS 101
- GEMSTONES 101
1CUT
When a diamond is cut to the ideal proportions, all of the light entering from any direction is totally reflected through the top and is dispersed into a display of sparkling flashes and rainbow colors.
Popular Shapes







2COLOR
Most diamonds, although appearing colorless, actually have slight tones of yellow or brown. As these tones become more easily apparent, the rarity and cost decrease.
Ideal cutting dramatizes the rare splendor of a diamond because it produces such dazzling brilliance

Colorless

Near Colorless

Taint Yellow

Very Light Yellow

Light Yellow

Light Yellow-Yellow
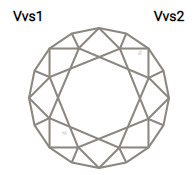
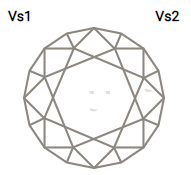
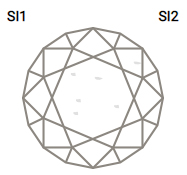
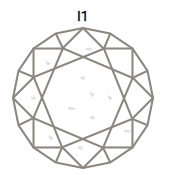
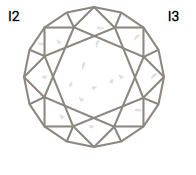
3CLARITY
Practically all diamonds contain naturally occurring internal characteristics called inclusions. The size, nature, location and amount of inclusions determine a diamond’s grade and affect its cost.
One unique advantage of the Ideal Cut is that its sparkle can mask otherwise noticeable inclusions.
4CARAT
The weight of a diamond is measured in carats. One carat is defined as 200 milligrams. The value of two diamonds of the same weight can vary greatly depending on the color, the clarity and, especially, the cut.





And now that you’ve been more educated about diamonds, it’s time to come see us at one of our Morgan Jewelers locations. Our team of diamond specialists can answer any additional questions you might have about selecting the right diamond.
Pearls are classic, like the “little black dress,” and should be a staple to any woman’s wardrobe. Pearls are versatile and appropriate for any age. When you cannot decide what to give your grandmother or maybe the flower girl at your wedding, pearls can save the day and be passed on for generations. Pearls come in many colors, shapes and sizes, so finding the style that best fits the individual or occasion will be no problem. There are four types of pearls you can choose from. Our Morgan Jewelers Pearl Guide goes into more detail about these pearls and their unique differences.
7 QUALITIES OF PEARLS
LUSTER
Of the seven pearl value factors, luster might be the most important. Luster is what gives a natural or cultured pearl its unique beauty. Pearls with high luster have sharp bright reflections on the surface. Different pearl varieties have different standards for luster.
SURFACE
If surface characteristics are numerous or severe, they can affect the durability of the pearl and severely depress its value. Surface characteristics have less effect on the pearl’s beauty and value if they are few in number, or if they are minor enough to be hidden by a drill-hole or mounting.
SHAPE
Pearls come in eight basic shapes: round, semi-round, button, drop, pear, oval, baroque, and circled. Perfectly spherical pearls and symmetrical drops are the most valued. There are exceptions, though. Well-formed pear, oval, or baroque cultured pearls are also prized by pearl lovers.
COLOR
Pearl body colors vary by variety. Although white and black are traditional, unusual colors are becoming more popular. Overtones in a pearl’s luster and the rainbow iridescence known as orient also add to the color of a pearl.
NACRE THICKNESS
Luster and nacre quality are closely related. If the nucleus is visible under the nacre, or if the pearl has a dull, chalky appearance, you can assume that the nacre is thin. This affects the luster as well as the durability of the pearl. Nacre thickness is evaluated to make sure that cultured pearls are durable as well as beautiful.
SIZE
In general, the larger the pearl, the more valuable it is. Different varieties come in different sizes: South Sea cultured pearls are the largest.
MATCHING
Jewelry designers sometimes deliberately mix colors, shapes, and sizes for unique effects, but for most pearl strands, earrings, or other multiple-pearl jewelry, the pearls should match in all the quality factors.
Most natural-colored gemstones are treated or enhanced to intensify color, diminish imperfections or improve durability. Morgan Jewelers is a colored gemstones expert. Learn more about the most commonly used and accepted treatments for different types of colored gemstones.
EMERALDS
Emeralds are a colored gemstone that range in color from light to dark green. Oiling is an ancient process used to enhance the clarity of emeralds. Oil is applied to the emerald and seeps into the fissures, which reach the stone’s surface. Aside from improving clarity, this process may prevent brittleness. Oiling is generally not permanent and may need to be reapplied every few years. Special care is required for cleaning, repairing or mounting oiled stones.
RUBIES
Rubies are pink to blood-red colored gemstones. Prices are determined by color. The brightest and most valuable red, called “blood red” or “pigeon blood,” can command a large premium over other rubies of similar quality. Treatments and improvements may include altering color, improving transparency by dissolving rutile inclusions, healing of fractures (cracks) or even completely filling them.
SAPPHIRES
While typically associated with the color blue, sapphires can also naturally occur in a wide variety of colors such as blue, yellow, purple, orange and green (which are also called “fancy sapphires”). “Parti sapphires” are those sapphires which show two or more colors in a single stone. Sapphires may be treated by several methods to enhance and improve their clarity and color. It is common practice to heat natural sapphires to improve or enhance color.
OTHER STONES
Heating is a widely accepted enhancement process used on amber, aquamarine, amethyst, citrine, tiger-eye, tanzanite, topaz and tourmaline. This treatment improves the transparency and/or color of the stone. Since heating is generally permanent, heated stones do not require special care.
Diffusion is another method occasionally used particularly on blue sapphires. During treatment, a colorless sapphire is coated with a titanium and oxide compound and exposed to heat. This enhances and/or changes the color of the stone and does not generally require special treatment.
Irradiation is often used with blue topaz. The stone is irradiated brown and then heated to produce the blue color. Irradiated stones do not require special care.
If you have any questions, or would like information on other treatments used for colored gemstones, ask your Morgan Jewelers
